🤓 The 2026 Local Search Ranking Factors are here!! Check out the report!
🤓 The 2026 Local Search Ranking Factors are here!! Check out the report!

They say imitation is the sincerest form of flattery. But on Google Maps, it is anything but flattering to find out your Google My Business listing has a doppelgänger. A duplicate GMB listing can hurt your rankings and put your business listing at risk of suspension. Meanwhile, it’s not uncommon to see your competitors spamming Google Maps by creating multiple listings for one business. So why do duplicates seem to help some businesses and hurt others? In this guide, we’ll help you determine when you should remove a duplicate and when you should merge, and show you how! But first let’s look at what a duplicate is, and how to see if your business has any harmful doppelgängers hanging around.

A duplicate GMB listing is an additional listing for a business or place that already has a listing. These listings can cause problems for business owners and users alike. Duplicate listings can divide ranking power and review counts, outrank or hide the owned listing, and cause confusion and distrust for search engines and searchers alike.
There are few possible sources for duplicate listings:
Need expert help managing your Google Business Profile and local SEO? With Whitespark on your team you never have to worry about a rogue duplicate listing causing trouble for you. Learn more about how we can help you manage your local SEO.
Finding a duplicate listing comes down to three major identifiers: Name, Address, and Phone number (NAP) and all their possible variations.
Name
A business’s name is one of the most important identifiers. Lucky for us spam-fighters, we can use that to our advantage. To find duplicate listings, search for the business name on Google Search and see if multiple listings populate. If so, look in Maps to see where these listings are located and determine if they are duplicates. In order to stay under Google’s eye, duplicate listings will add keywords or mix up their business name to not be detected.
Find out the businesses registered name by looking for signage in street view, visiting their website and assessing their logo, or searching for them in a local directory or Secretary of State business entity search (U.S. only).
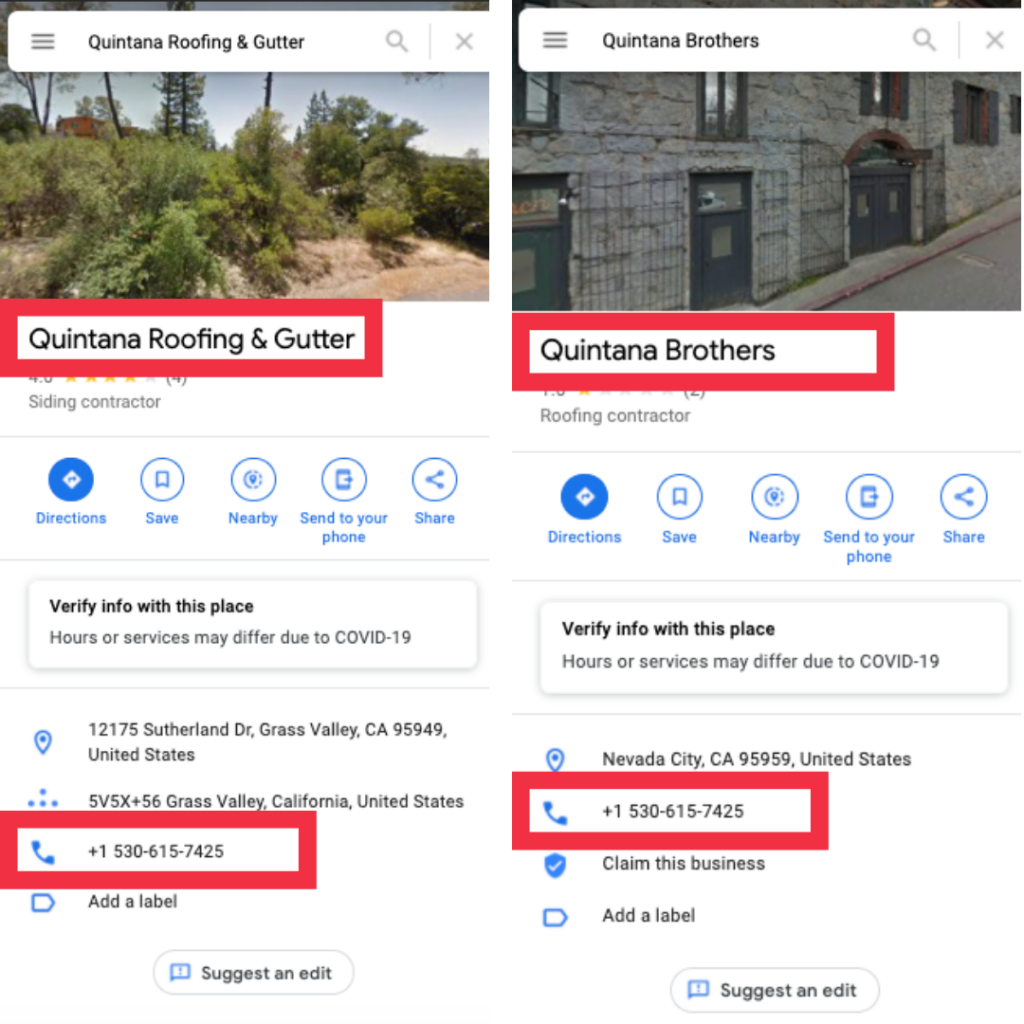
Address
We have found that businesses will frequently hide under the radar from Google’s spam detection by forgoing adding a suite number that they have on their other listing, moving their map pin, or simply creating a second listing as a Service Area Business. Make sure to look into these inconsistencies:
If so, these are red flags that the business is using duplicate listings to rank.
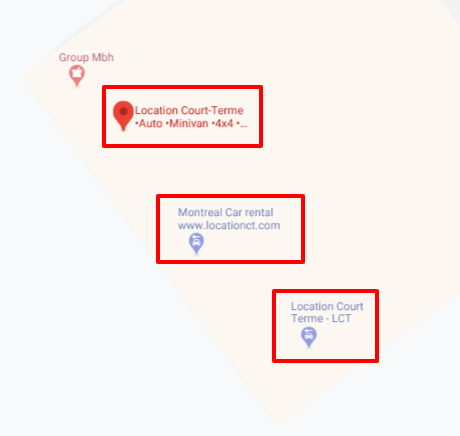
Phone Number
Lastly, we can use phone numbers to search for duplicate listings. We have found that businesses will use different phone numbers, whether it’s a call tracking number, a mobile number, or a different number all together to be filtered out as a duplicate listing. Again, see if the other listings have similarities in their name, address and website. In addition, you can visit their website or other directory pages (YELP or BBB, for example) and see if the number is consistent on those pages. Often, only one main number will be associated with the business.

Now that you know how to find a duplicate listing let’s jump into action to get duplicate listings under control. Before we look into merging the listings, let’s look at how you can clean up duplicates of your listing and what you can do about a competitor’s spammy duplicate listings.
When finding a duplicate of your business, we have found that a business owner may already own the duplicate listing under a different email or a different owner. In the case of practitioners or practices, a previous owner may have created the listing without the current owner’s knowledge. Additionally, Google’s AI may even create a duplicate listing. Regardless, when you find a duplicate of your listing we suggest you request ownership of the listing and follow the steps to get the listings merged or removed.
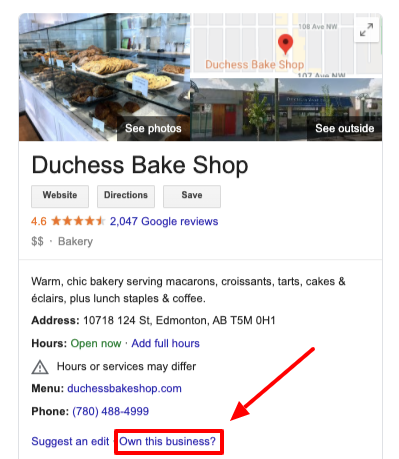
In our experience, using the Google Maps “Suggest an Edit” feature to report a duplicate is effective if the listing is not claimed and has consistent NAP with the other listing.
If the NAP isn’t consistent between the two listings, attempt to edit the information with “Suggest an Edit”. Once the edit is approved, use “Suggest an Edit” again to report the duplicate.
You’ll receive an automated email from Google when your edit is approved. The duplicate below was reported via “Suggest an Edit” and the edit was published:
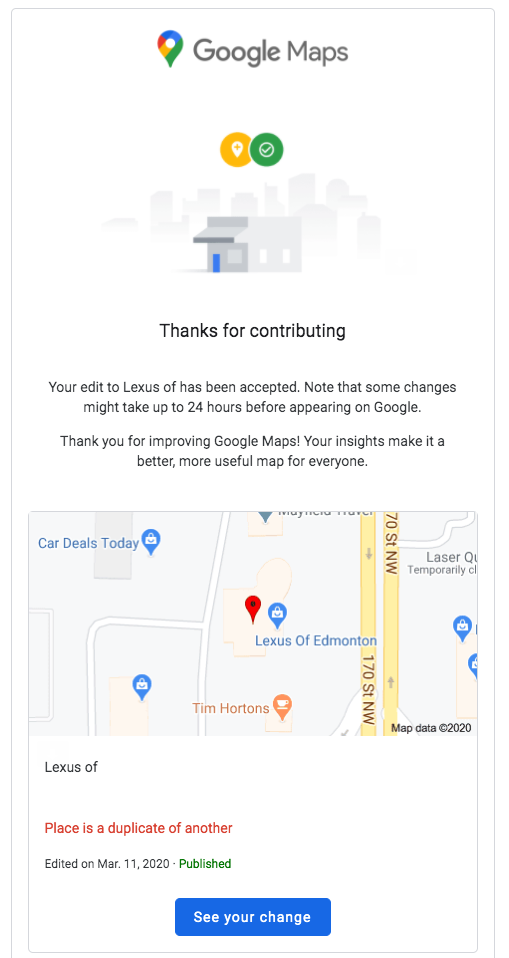
If the business has multiple duplicate listings you should head to the Redressal Complaint form. Here you can identify the business, each duplicate listing, and give detailed evidence directly to Google Support.
We have found that spammy competitors will make duplicate listings to manipulate rankings in different primary categories. This gives them the ability to rank for keywords related to both categories and therefore increases their visibility. This is against Google’s guidelines and gives the competitor an unfair advantage. In these cases, we suggest:
Duplicate listings will often have 1 or 2 reviews with little to no content to manipulate users and Google into thinking it is legitimate. It’s harder to remove a duplicate listing that has reviews because they add legitimacy to the business. If you find a competitor with duplicate spammy listings with reviews, you can send a Redressal Complaint form or contacting Google Support with evidence of the duplicate listings as using the “Suggest an Edit” feature on Google Maps will likely lead to your edit getting denied.
However, we recommend looking at the duplicate listings carefully (their ranking, categories, names and reviews) as reporting the duplicate could result in Google merging the listings, which would increase the business’s review count and star-rating, which could affect its ranking and yours – for better or worse.
It’s possible that your competitor’s business has duplicate listings that weren’t created to game rankings. In this case, we don’t recommend reporting the duplicates as they’re likely not helping your competitor’s ranking.
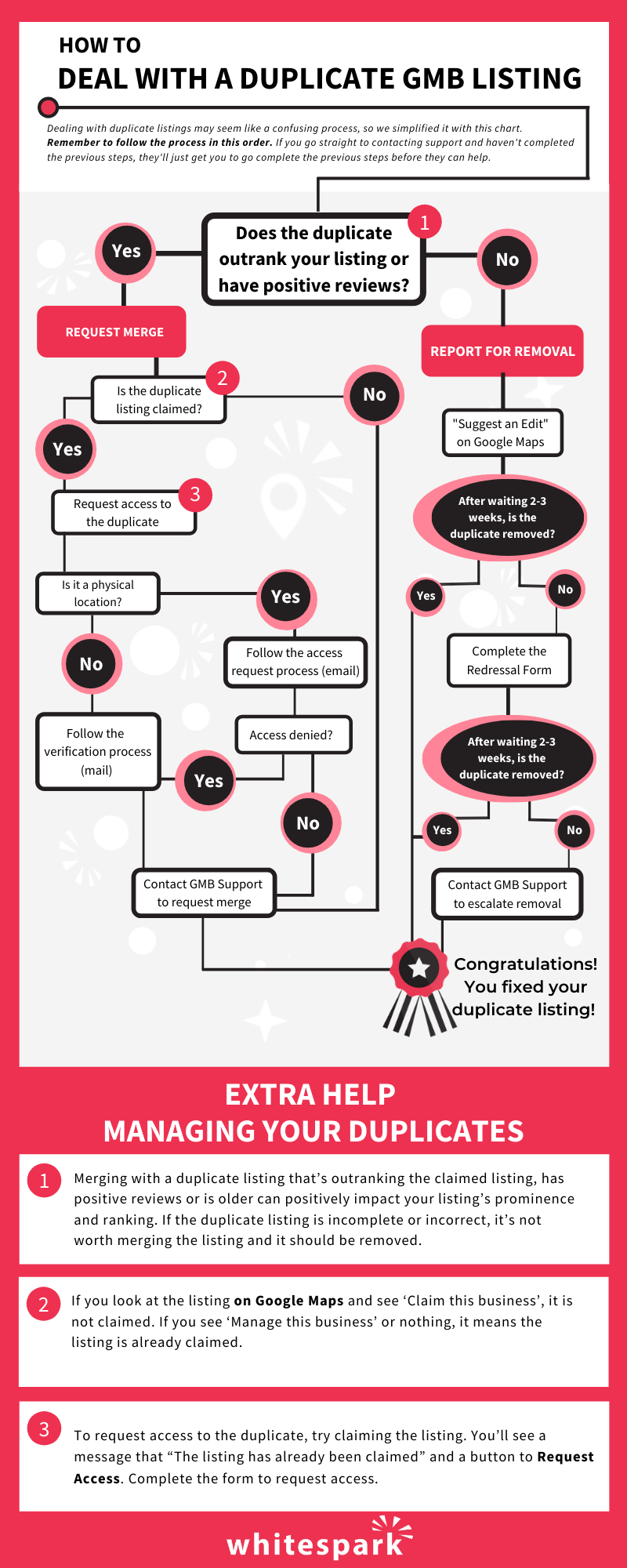
To help you navigate the best practices for reporting and merging duplicates, we’ve put our process into a simple flowchart. But first, let’s review when it’s worth merging duplicates, how to tell if a listing is claimed, and Google’s (complicated) process for getting access to a listing claimed by someone else.
A duplicate listing is worth merging if there are assets that would be valuable to have added to your original listing, such as:
Positive reviews
Having your reviews divided between your claimed listing and a duplicate doesn’t help build your review count, star rating or review frequency. When requesting a merge, specify to Support that you want the reviews on the duplicate ported over to the claimed listing.
History
To determine if a duplicate listing is older than the claimed listing, and therefore has valuable history, examine the listing for user-generated content that pre-dates the claimed listing. Are there reviews, photo uploads or questions on the listing that are older? If the listing is claimed, is the email address for an old business email account or an old marketing company? You can use this information to estimate if the listing is older than your claimed listing.
Higher ranking
Perform a Google search for your keywords, top services and business categories or monitor your rankings with a tool like Whitespark’s Rank Tracker and examine Google Maps, Local Finder and Local Pack screenshots to see if a duplicate is outranking your claimed listing.
Take a look at the listing on Google Maps. In the information section where the address and phone number are, near the bottom, you’ll either see ‘Claim this business’ or ‘Manage this business or neither.
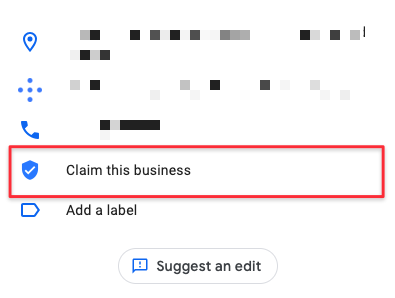
If it says ‘Claim’, the listing is not claimed.
If it says, ‘Manage’ or has neither, it is claimed and you’ll have to go through a verification process to gain access.
The process is different for physical locations and service area businesses. Let’s take a look at both.

Start by trying to claim the listing. A message should appear saying the listing has already been claimed.
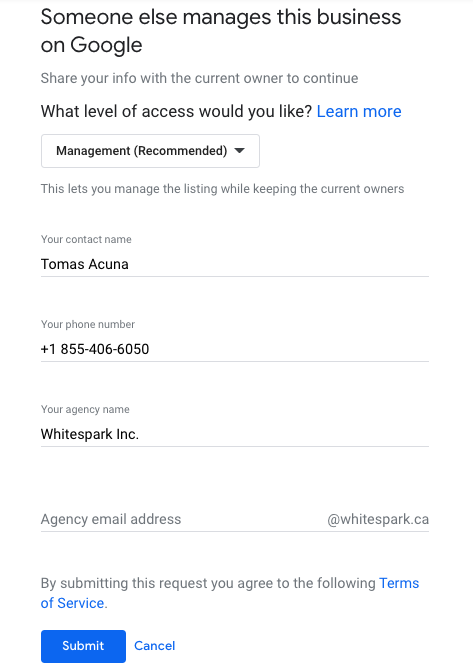
Tip: The current owner is given 3 days to approve, deny or ignore your request. Contacting Google Support before the 3 days will not speed up this process.
This process is a foolproof way of returning ownership to the correct party, but unfortunately it only works for physical locations.
The process to get access to a claimed listing is a bit different for SABs. You’ll have to go through the process of essentially creating a new listing. And it feels like you’re actually making a duplicate, but this is Google’s process.

Tip: The current owner is given 3 days to approve, deny or ignore your request. Contacting Google Support before the 3 days will not speed up this process.
The complex processes and nuances can be confusing when dealing with duplicate GMB listings, but this doesn’t mean you should avoid dealing with them. Duplicates can affect your rankings by filtering out your more prominent listing or negatively impact customer experience by providing incorrect or outdated information. Take the time to clean up your duplicates correctly and you’ll be rewarded with more website visits, phone calls, and walk-ins by putting your best foot forward from the moment a customer finds you on Google.Need expert help managing your Google Business Profile and local SEO? With Whitespark on your team you never have to worry about a rogue duplicate listing causing trouble for you. Learn more about how we can help you manage your local SEO.
Whitespark provides powerful software and expert services to help businesses and agencies drive more leads through local search.
Founded in 2005 in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada, we initially offered web design and SEO services to local businesses. While we still work closely with many clients locally, we have successfully grown over the past 20 years to support over 100,000 enterprises, agencies, and small businesses globally with our cutting-edge software and services.